Introduction
You must be familiar with PCIe 4.0 if you enjoy building high-performance PCs or are a tech geek. The Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) standard is one that it is based on, and it is revolutionizing the computing industry. You may attain faster data transfer speeds with PCIe 4.0, which translates to quicker file transfers, better data processing, and faster gaming. However, what exactly is PCIe 4.0 and how is it different from earlier versions? What advantages does it provide? We’ll address all of these queries in this blog post. We’ll examine PCIe 4.0’s technical features, such as its bandwidth and data transmission speeds, and also look at PCIe 4.0’s hardware specifications, including compatible motherboards and parts. PCIe 4.0 doubles data transfer speed, enabling faster file transfers, improved data processing, and enhanced gaming. Requires compatible hardware for optimal performance. Let’s dive into everything you need to know about PCIe 4.0 and see how it may boost your performance and productivity.
What is PCIe 4.0?
The Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) is an interface standard for attaching expensive components to your computer. PCIe 4.0 is the fourth generation of PCIe.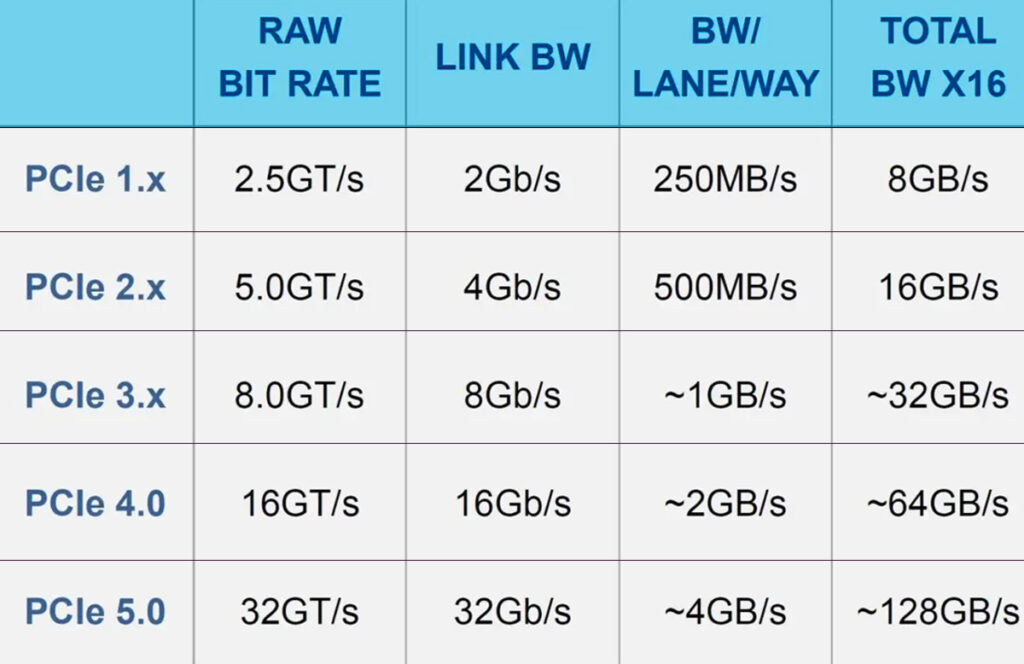 PCIe Gen 1, or the first generation of PCIe, debuted in 2003. There have been four new iterations of PCI Express over time. The fourth generation of PCI Express will be today’s main topic.
PCIe 4 increases the PCIe 3.0 generation’s data transfer speed from 1GB/s to 2GB/s per lane, giving customers a total of 32GB/s in a 16-lane setup.
Furthermore, PCIe enables up to 16GT/s per lane as compared to the previous generation’s 8GT/s.
Each new generation of PCIe doubles the data transfer rate and total bandwidth per lane of the prior generation, paving the way for new, faster PCIe devices.
At 16 Giga transfers per second (GT/s), PCIe 4.0 is the fastest PCIe generation available on the market right now, and high-performance computer manufacturers are scrambling to adopt it for their customers.
The individual bandwidths that consumers can anticipate from the x1, x2, x4, x8, or x16 PCIe slots on their motherboards are doubled as a result of this increase in transfer rate.
Related Read: PCIe-All Generations One-Stop Point Log [Ultimate Guide]
PCIe Gen 1, or the first generation of PCIe, debuted in 2003. There have been four new iterations of PCI Express over time. The fourth generation of PCI Express will be today’s main topic.
PCIe 4 increases the PCIe 3.0 generation’s data transfer speed from 1GB/s to 2GB/s per lane, giving customers a total of 32GB/s in a 16-lane setup.
Furthermore, PCIe enables up to 16GT/s per lane as compared to the previous generation’s 8GT/s.
Each new generation of PCIe doubles the data transfer rate and total bandwidth per lane of the prior generation, paving the way for new, faster PCIe devices.
At 16 Giga transfers per second (GT/s), PCIe 4.0 is the fastest PCIe generation available on the market right now, and high-performance computer manufacturers are scrambling to adopt it for their customers.
The individual bandwidths that consumers can anticipate from the x1, x2, x4, x8, or x16 PCIe slots on their motherboards are doubled as a result of this increase in transfer rate.
Related Read: PCIe-All Generations One-Stop Point Log [Ultimate Guide]
What does PCIe 4.0 do?
Like other generations of PCIe, PCIe 4.0 interfaces with the computer’s motherboard to facilitate the high-speed transfer of data from graphics cards, NVMe SSDs, RAID cards, and other expansion cards. This technique is achieved by the motherboard’s PCIe slots, into which these expansion cards are plugged.
PCIe 4.0 expansion cards, such as this $89 ASUS Hyper M.2 x16 PCIe 4.0 x16 card, which is utilized for high-performance PCIe 4.0 NVMe SSDs, are placed into PCIe slots, which may or may not be installed on a PCIe 4.0 motherboard.
This technique is achieved by the motherboard’s PCIe slots, into which these expansion cards are plugged.
PCIe 4.0 expansion cards, such as this $89 ASUS Hyper M.2 x16 PCIe 4.0 x16 card, which is utilized for high-performance PCIe 4.0 NVMe SSDs, are placed into PCIe slots, which may or may not be installed on a PCIe 4.0 motherboard.
Why do we need PCIe 4.0?
We require PCIe 4.0, to prevent the system from becoming bottlenecked, the highways for the data moving between CPUs, GPUs, and data storage devices like NVMe SSDs must also evolve. These devices receive increased bandwidth thanks to PCIe Gen 4, which keeps them fed with data. Consider a PCIe M.2 NVMe SSD as an illustration. Most M.2 NVMe SSDs utilize the x4 connection, which has a bandwidth of 4GB/s, which bottlenecks the SSD. However, PCIe Gen 4 increases the bandwidth to approximately 8GB/s, allowing the system to utilize the full potential of the M.2 NVMe drive. As such, it’s plain to see that we need PCIe Gen4 to keep up with the developments in computing gear. Additionally, the growth of the internet, the ever-increasing number of IoT devices, and the increasing complexity of AI workload necessitate the need for faster and more efficient interfaces (pipes) through which to transfer data. By increasing the pipeline width by twofold, PCIe Gen 4 meets the need. To accommodate the increase in data volume and speed, more bandwidth will be required in the future. Technological advances often move quicker than market demand, especially as it relates to real-world deployments. The total cost of ownership, or TCO, plays a significant role in how rapidly technology is adopted. Despite the advantages of modern technologies over legacy ones, a real-world implementation may not be financially viable due to the expense of doing so. Related Read: A brief comparison between PCIe 5.0 vs PCIe 4.0 Image Credit
A great example of this case is the introduction of high-performance NVMe storage solutions in many industry 4.0 or intelligent embedded computing applications.
Due to its low cost and performance benchmark of 500–550 MB/s in transfer speeds, the 6Gb/s SATA protocol has historically been favored by many embedded applications.
Even now, a lot of embedded applications still transmit and store data locally on computers utilizing the SATA interface.
As a result of the need for faster processing, storage, and connection resulting from edge computing, NVMe architecture (PCIe Gen 3.0) and storage solutions have only lately begun to appear in more embedded computing applications.
The demand for quicker access to high-speed NVMe storage can only recently be seen in Intel’s 8th and 9th generation processors, as well as in the Q370 chipset architecture and embedded market solutions.
These generations of industrial computing solutions specifically dedicate PCIe Gen 3.0 lanes directly for an onboard m.2 NVMe storage solution for access to high-speed storage.
Although PCIe Gen 4.0 is already on the market and has theoretically demonstrated benchmarks in performance, many real-world embedded computing applications may not need access to these speeds until a later stage in technological adoption.
On the other hand, solutions for PCIe Gen 4.0 are proven to be quite useful in the setting of high-performance data centers.
Image Credit
A great example of this case is the introduction of high-performance NVMe storage solutions in many industry 4.0 or intelligent embedded computing applications.
Due to its low cost and performance benchmark of 500–550 MB/s in transfer speeds, the 6Gb/s SATA protocol has historically been favored by many embedded applications.
Even now, a lot of embedded applications still transmit and store data locally on computers utilizing the SATA interface.
As a result of the need for faster processing, storage, and connection resulting from edge computing, NVMe architecture (PCIe Gen 3.0) and storage solutions have only lately begun to appear in more embedded computing applications.
The demand for quicker access to high-speed NVMe storage can only recently be seen in Intel’s 8th and 9th generation processors, as well as in the Q370 chipset architecture and embedded market solutions.
These generations of industrial computing solutions specifically dedicate PCIe Gen 3.0 lanes directly for an onboard m.2 NVMe storage solution for access to high-speed storage.
Although PCIe Gen 4.0 is already on the market and has theoretically demonstrated benchmarks in performance, many real-world embedded computing applications may not need access to these speeds until a later stage in technological adoption.
On the other hand, solutions for PCIe Gen 4.0 are proven to be quite useful in the setting of high-performance data centers.
 Image Credit
Image Credit
PCIe 4.0 bandwidth
The interconnect performance bandwidth is double that of the PCIe 3.0 specification delivering 16GT/s and compatibility with software and mechanical interfaces is preserved. The PCIe 4.0 architecture is backward compatible with earlier PCIe versions. The number of PCIe lanes that a PCIe Gen 4 device supports is necessary to comprehend the device’s maximum bandwidth. The more “lanes” a PCIe device can use, the more bandwidth it can provide since PCIe devices use “lanes” for data transmission and reception. A PCIe device’s support for a certain number of lanes is typically indicated by an expression like “x4” for 4 lanes, “x8” for 8 lanes, and so on.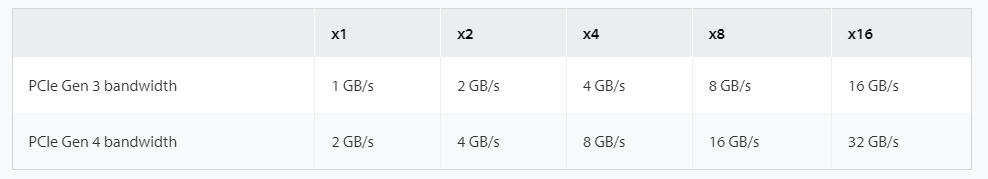 Image Credit
Image Credit
PCIe 4.0 Motherboard
There are four different types of PCIe 4.0 expansion slots available on a common PC motherboard: PCIe x1, PCIe x2, PCIe x4, PCIe x8, and PCIe x16. These figures represent the number of lanes that each PCIe slot has. The more lanes that a PCIe slot has, the more data can be transported to/from the add-on card.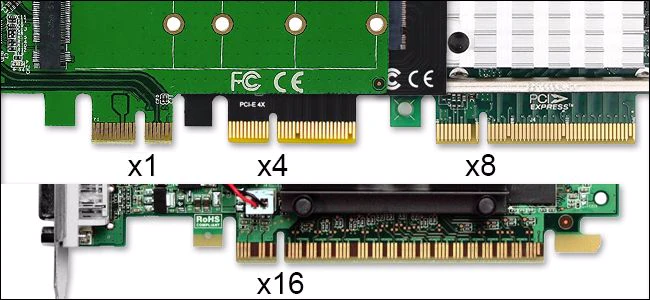 Image Credit
Each PCIe Lane is made from two pairs of wires, one for transmitting data and one for receiving data.
An 8-lane connection will have twice the bandwidth of a 4-lane configuration because the bandwidth scales linearly with PCIe.
PCI Express has the advantage of maintaining both forward and backward compatibility, supporting both modern and antiquated technologies.
PCIe supports PCIe Gen 1, PCIe Gen 2, and PCIe Gen 3 devices. PCIe Gen 4 will be compatible with PCIe Gen 5. A PCIe Gen 4 device, however, will be constrained to Gen 4 requirements when put into a Gen 5 slot.
To put it another way, PCIe 4.0 cards can be used with motherboards that have PCIe 3.0 slots, and PCIe 3.0 cards can be used with motherboards that have PCIe 4.0 slots.
That noted, although PCIe 4 cards will work on PCIe 3.0 motherboards, their performance will be limited according to PCIe 3.0 standards.
Image Credit
Each PCIe Lane is made from two pairs of wires, one for transmitting data and one for receiving data.
An 8-lane connection will have twice the bandwidth of a 4-lane configuration because the bandwidth scales linearly with PCIe.
PCI Express has the advantage of maintaining both forward and backward compatibility, supporting both modern and antiquated technologies.
PCIe supports PCIe Gen 1, PCIe Gen 2, and PCIe Gen 3 devices. PCIe Gen 4 will be compatible with PCIe Gen 5. A PCIe Gen 4 device, however, will be constrained to Gen 4 requirements when put into a Gen 5 slot.
To put it another way, PCIe 4.0 cards can be used with motherboards that have PCIe 3.0 slots, and PCIe 3.0 cards can be used with motherboards that have PCIe 4.0 slots.
That noted, although PCIe 4 cards will work on PCIe 3.0 motherboards, their performance will be limited according to PCIe 3.0 standards.
Processors Supporting PCIe 4.0
For those looking to take advantage of the most throughput, the following processors support PCIe 4.0.- 11th Gen Core Processors by Intel
- 12th Gen Core Processors by Intel
- 3rd Gen Xeon Scalable Processors by Intel
- Ryzen 3000 and 5000 Series Processors by AMD
- EPYC 7002 and 7003 Series Processors by AMD
Difference between PCIe Gen 3 and PCIe Gen 4
With options for 1x, 2x, 4x, 8x, and 16x slot configurations, PCI Express 4.0 doubles the speed of PCI Express 3.0, increasing performance from one gigabyte per lane to two gigabytes per lane while raising the maximum potential bandwidth of a PCI Express slot to 64 gigabytes per second.

However, they are not even close to using the bandwidth offered by the PCIe 3 slot. Contemporary graphics cards cannot fully utilize PCIe 4. However, when it comes to storage add-in cards, PCIe 4 shines.
For example, PCIe 4.0 NVMe drives will benefit from the extra bandwidth because NVMe drives operating in a Raid 0 configuration can execute sequentially at read/write speeds up to 15 GB/s.
This is important because large data sets must be repeatedly stored and fetched when performing AI computations and using them for testing and training machine learning algorithms.
Overall, PCI Express 4 considerably enhances the read/write rates of SSDs, delivering an excellent improvement in performance for such complicated tasks.
There will always be a demand for faster data transfer rates as AI algorithms become more and more complex.
The speed at which data may be accessed is substantially faster because to PCIe 4.0’s increased bandwidth, enabling more fluid real-time data analysis.
PCI Express also provides the additional advantage of lowering the number of lanes needed for add-on cards.
This is so because each of the lanes is increasing quicker, reducing the number of lanes required for specific devices.
An NVMe SSD card, for instance, can function at PCIe 4 x8 speeds while utilizing half the lanes and providing the same bandwidth as a PCIe 3 x16 slot.
The extra lanes can be used to add more devices and enable them to operate in smaller PCIe slots, enabling system designers to create smaller, more compact systems.
Benefits of PCIe 4.0

PCIe 4.0 in the data center
Data centers that can make use of the improved performance provided by PCIe 4, will reap the benefits of PCIe 4.0 to the greatest extent.
This is because PCIe 3.0 is being saturated by NVMe storage technologies; PCIe 4 will enable them to attain optimal performance and faster data transfer rates due to the additional bandwidth provided by PCIe 4.0.
PCIe 4.0 High bandwidth
PCIe 4.0’s increased bandwidth enhances the performance of workloads like machine learning (ML) and cloud computing, resulting in a decrease in the amount of time needed to compute any given task.
Along with that, it eases lane congestion and lowers the device’s battery usage.
Boost in Data Transfer Speeds

PCIe 4.0 won’t offer much value to the typical PC user, but data centers will gain a lot by upgrading from PCIe 3.0 to PCIe 4.0.
This is true as a result of PCI Express 4.0’s ability to move data twice as quickly, which enables GPUs and PCIe SSDs to deliver faster I/O, providing a noticeable performance improvement when running computational and data-intensive applications like data analysis, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
These tasks will run more quickly thanks to PCIe Version 4’s ability to transfer data at about 2GB/s per lane as opposed to PCIe Version 3’s 1GB/s per lane, which doubles the previous generation’s performance while offering 4-lane performance of 8GB/s, which is the most common standard used by PCIe SSDs
Sequential read and write speeds of up to 6,900 MB/s and 4,200 MB/s, respectively, were measured for PCIe 4.0 SSDs.
However, PCIe 3.0 SSDs were able to attain sequential read and write rates of up to 3,350 MB/s and 3040 MB/s, respectively. This demonstrates that compared to PCI Express 3.0, PCI Express 4.0 offers a substantial performance improvement.
Conclusion
The PCIe standard has been significantly upgraded with PCIe 4.0, which offers faster data transfer rates and better performance.
It is built to manage the demands of contemporary computing, such as data processing, gaming, and quick file transfers.
To benefit from PCIe 4.0’s advantages, you should consider using PCIe 4.0-compatible components whether creating a new system or upgrading an existing one.
You should make sure that your motherboard and other components are compatible with PCIe 4.0 because not all gear is.
For high-performance computing, PCIe 4.0 is a game-changer, and this is an exciting time for professionals and tech enthusiasts alike.
We trust that this blog post has given you a thorough grasp of PCIe 4.0 and its advantages.
Stay tuned for the next blog on PCIe 5.0…!!







