Smart Car Designs with Automotive FPGAs: The automotive industry is undergoing a revolutionary transformation with the rise of smart car designs. As vehicles become more connected, autonomous, and intelligent, the need for advanced technologies to support these capabilities becomes paramount.
Among the key technologies driving this evolution are Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs). These powerful semiconductor devices have emerged as a vital component in smart car architectures, enabling the seamless integration of complex functionalities and enhancing overall vehicle performance.

So, what exactly are FPGAs, and why do they hold such significance in the realm of smart car design? FPGAs are programmable logic devices that can be configured and reconfigured by designers to perform specific tasks and functions.
Unlike traditional processors and microcontrollers that execute fixed instructions, FPGAs offer unparalleled flexibility and adaptability, making them ideal for addressing the dynamic requirements of modern automotive systems.
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), entertainment systems, engine management, and safety and security features are just a few of the cutting-edge elements included in smart car designs.

FPGAs are an effective way to deliver the powerful processing power, responsiveness in real-time, and excellent data management that these advanced systems require.
As a result, FPGAs are being used more frequently by technology firms and automakers to boost the performance and innovation of their smart car solutions.
We will dive deeper into the realm of automotive FPGAs in this blog as we examine their use, advantages, and difficulties in designing smart cars.
We will look at particular applications for FPGAs, like ADAS, infotainment systems, and powertrain management.
Understanding automotive FPGAs
Automotive FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays), which provide a versatile and effective solution for controlling the numerous capabilities required in current automobiles, are essential in the development of smart car designs.
In this blog, we’ll examine the idea of automotive FPGAs, consider how they differ from conventional processors, and highlight the salient characteristics that make them a crucial part of smart car architectures.

Market Growth of the Automotive Industry
According to precedence research, The global automotive motors market size was estimated at USD 29.2 billion in 2021 and it is expected to reach around USD 41.66 billion by 2030 and is poised to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.03% during the forecast period 2022 to 2030.

What are automotive FPGAs?
Automotive FPGAs are programmable integrated circuits that give designers the ability to develop unique digital circuits and features specifically for automotive applications.
FPGAs offer a great degree of configurability and flexibility, in contrast to conventional processors and microcontrollers, enabling real-time processing, parallel data handling, and effective resource use.
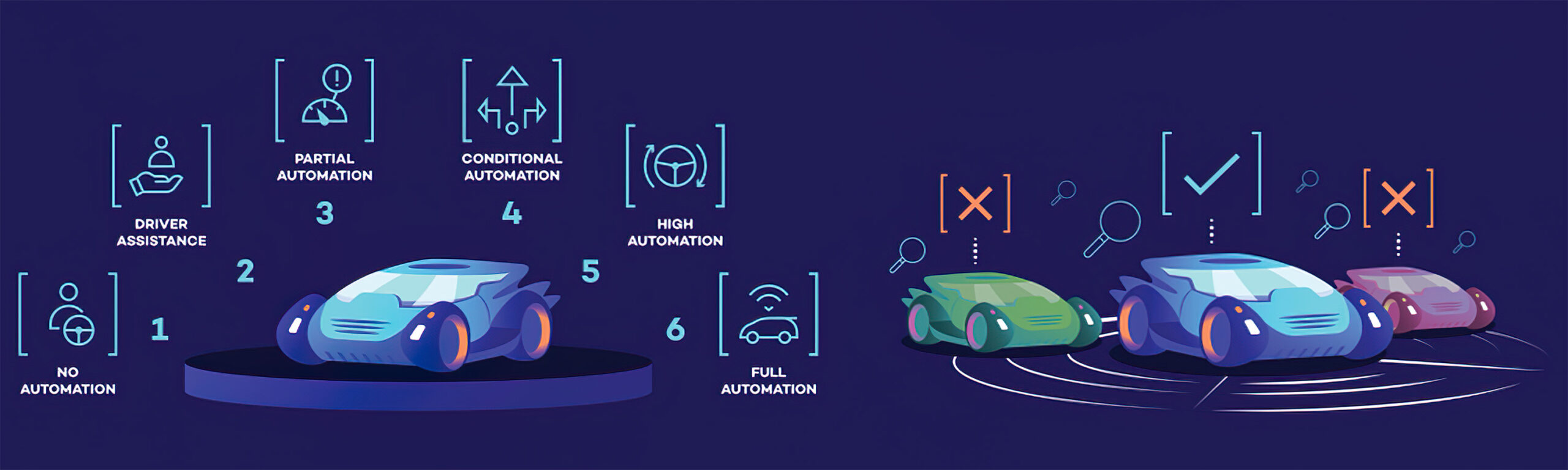
The Role of FPGAs in Smart Car Designs
Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, or FPGAs, are key components in the creation of smart automobile designs since they have several benefits and make it possible to apply cutting-edge capabilities of FPGAs in ADAS
Similar Read: Role of FPGAs in High-Performance Computing
We’ll examine the unique functions and uses of FPGAs in the development of smart cars, emphasizing how these devices affect numerous systems and operations.
The growth rate of FPGA in the automotive industry is expected to be significant in the coming years.
According to Mordor Intelligence, the global FPGA market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.32% from 2023 to 2028. The automotive industry is one of the key drivers of this growth, as FPGAs are increasingly being used in a variety of automotive applications, such as:
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS):
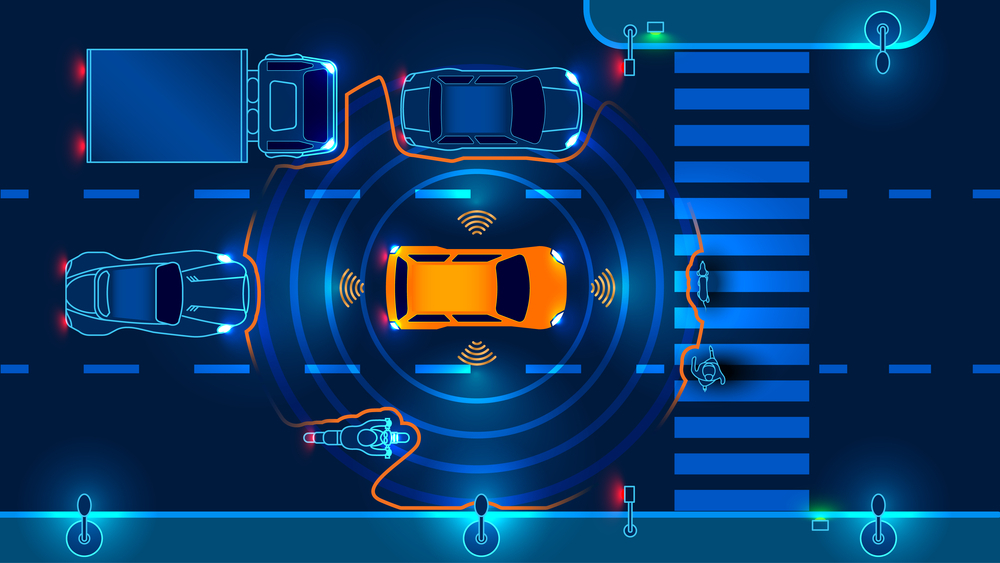
- ADAS is a crucial element of the design of smart cars, seeking to improve safety and driver assistance. By offering real-time processing capabilities and effective data handling, FPGAs play a crucial part in ADAS.
- Fast decision-making and response are made possible by the parallel processing architecture of the FPGA, which enables the simultaneous processing of sensor input from systems like cameras, radar, and LiDAR.
- FPGAs make lane departure warnings, adaptive cruise control, collision detection and avoidance, and other ADAS features possible, improving overall vehicle safety.
Infotainment Systems:
- Modern infotainment systems in smart automobiles are developed using FPGAs as a key component. To improve the user experience, they make it possible for high-resolution displays, graphics processing, and audio capabilities.
- Video decoding, image rendering, and audio processing are all tasks that FPGAs are adept at performing with efficiency.
- FPGAs guarantee slick and responsive performance by offloading these duties from the primary processor, enabling features like interactive touchscreens, navigation systems, multimedia streaming, and communication with external devices.
Powertrain and engine management:

- To ensure optimum performance and economy, FPGAs are crucial components of engine and powertrain management systems. Real-time fuel management, ignition control, and pollution control are made possible by FPGAs, which also allow engine optimization.
- FPGAs can execute complicated algorithms for engine management and calibration due to their high-speed processing skills, which leads to better fuel economy, lower emissions, and overall improved performance.
- FPGAs also assist with transmission control, guaranteeing seamless gear changes and optimal power delivery.
Safety and security:

- The design of smart cars must prioritize safety and security, and FPGAs offer crucial characteristics to meet these issues. To safeguard data sent between the vehicle and outside entities, FPGAs can enable secure communication protocols, encryption algorithms, and authentication techniques.
- They provide improved vehicle diagnostics and monitoring, making it easier to find flaws and malfunctions before they become serious.
- FPGAs can also include intrusion detection and prevention systems, protecting the car from cybersecurity dangers.
Sensor Fusion and Data Processing:
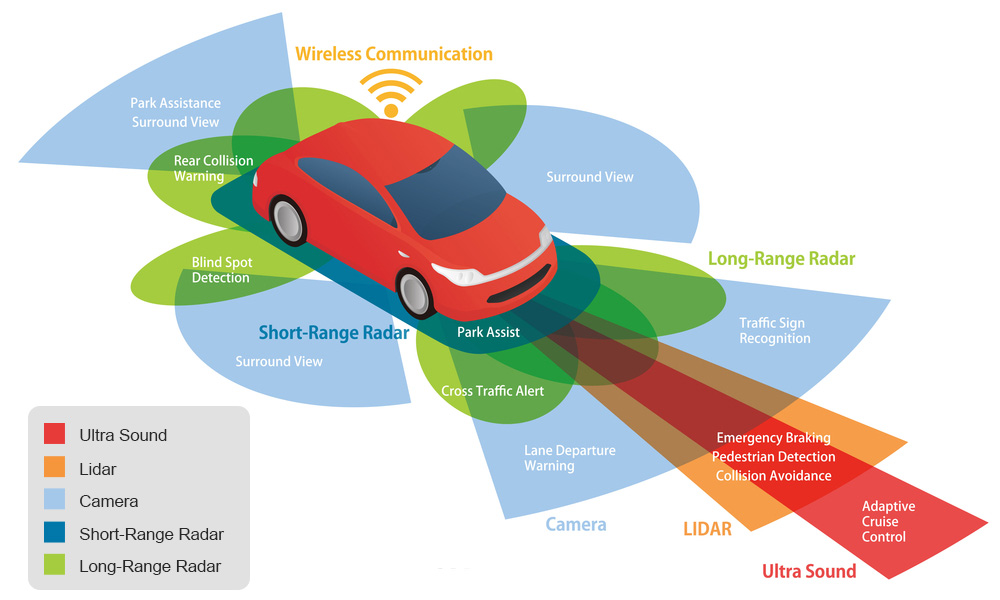
- Cameras, radars, LiDARs, and ultrasonic sensors are just a few of the sensors smart cars use to collect information about their environment.
- FPGAs excel at sensor fusion, which is the real-time integration of data from various sensors to produce a thorough and precise perception of the environment.
- FPGAs offer accurate object recognition, environment mapping, and decision-making, which are essential for autonomous driving and high-tech safety features. They do this by processing sensor data in parallel and running complicated algorithms.
Challenges and considerations
Despite their advantages, integrating FPGAs into automotive designs presents some challenges.
Design complexity: Developing FPGA-based solutions requires specialized knowledge and expertise in digital circuit design and programming.
Power consumption and thermal management: FPGAs can consume significant power, necessitating careful power management and thermal control strategies.

Safety and functional safety requirements: Meeting safety standards and ensuring functional safety compliance is critical when integrating FPGAs in safety-critical automotive systems.

Reliability and maintenance: Long-term reliability and maintenance considerations should be addressed to ensure the longevity and performance of FPGA-based solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, automotive FPGAs are essential to the development of smart cars because they enable cutting-edge functionality for ADAS, infotainment, powertrain management, safety, and sensor fusion.
These adaptable parts offer flexibility, real-time processing, and efficiency. FPGAs will continue to fuel innovation as smart car technology develops, influencing the future of linked and intelligent vehicles.
Automotive FPGAs are essential to the continuous revolution of the automotive industry because of their evident impact on safety, performance, and user experience.










