Imagine a scenario in which artificial intelligence composes a symphony to the hum of the motors, choreographing a ballet of accuracy and efficiency on the highways.
The automobile sector, which was long dominated by mechanics and engineering skills, is on the verge of an incredible upheaval with Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the driver’s seat.
A new era in which automobiles not only physically transport us but also help us navigate the intricacies of our modern lives has been brought about by the fusion of cutting-edge technology and automotive innovation.
According to precedence research, The size of the global artificial intelligence (AI) market was estimated at USD 538.13 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19% from 2023 to 2032, reaching over USD 2,575.16 billion.
Furthermore, the Asia Pacific artificial intelligence market is expanding due to the increasing use of artificial intelligence in a variety of industries, including retail, healthcare, automotive, and food and beverage.
The introduction of AI into the automotive industry has had a profoundly revolutionary impact on several industry areas.
Generative AI, or AI, is making a lasting impact on everything from the design process to the assembly line during the construction of an automobile.
In this fascinating journey through AI’s transformative role, we will see how algorithms and data are rewriting the fundamental foundations of transportation.
This brings us into a future where automobiles think, learn, and make judgments, forever changing the way we experience mobility.
Buckle up; the AI-driven automotive journey has only just begun.
What is AI in the Automotive Industry?

Artificial intelligence in the automobile industry refers to the application of artificial intelligence methods across many automotive domains.
Machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision are some of the AI technologies that are being integrated into the automotive sector to improve the driving experience.
In the area of artificial intelligence for automobiles, these technologies offer efficiency and safety while automating a variety of tasks like route planning, navigation, parking, etc.
Why Do We Need AI in the Automotive Industry?
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the automobile sector has already ramped up, from design and manufacture through production and post-production.
There are numerous reasons why this could be the start of something incredibly comfortable, safe, and fast.
Read on to some key benefits of artificial intelligence in the automotive industry:
Improved Safety
Improved road safety appears promising with AI in automobiles enabling advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Accident risk can be reduced by using AI algorithms to examine sensor data and detect potential threats in real time.
The AI automotive settings include technologies like automatic emergency braking and lane-keeping assistance that promote on-the-spot monitoring and safer driving conditions.
Autonomous Driving
AI’s contribution to transportation is autonomous vehicles, and self-driving cars have already generated significant media attention.
These vehicles use AI technologies to help them comprehend their surroundings, make quick decisions, and navigate without human assistance.
Call it a phenomenon or a revolution, but AI in self-driving cars means fewer mistakes made by humans, better traffic flow, and accessibility for those who cannot drive.
Some of the newest and most advanced self-driving vehicles are the Tesla Model 3, Volvo XC40, BMW iX, and Lexus LS.
Levels of ADAS
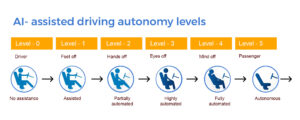 The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has established different levels of automation for ADAS functions. Levels 0–2 denote characteristics that aid drivers, while levels 3–5 cover the ability to drive autonomously.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has established different levels of automation for ADAS functions. Levels 0–2 denote characteristics that aid drivers, while levels 3–5 cover the ability to drive autonomously.
Level 0 – No assistance
The majority of ADAS features at level 0 are alert-based systems that inform drivers of possible hazards.
- Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM): Uses visual or auditory cues to warn drivers of cars in their blind areas.
- Lane Departure Warning (LDW): Alerts drivers when they inadvertently stray from their designated lane.
- Forward Collision Warning (FCW): Warns drivers of possible collisions with oncoming traffic.
- Traffic Sign Recognition (TSR): Identifies and shows traffic signs, assisting drivers in following the law.
Level 1 – Partial Automation
Although Level 1 adds some automation, the driver still has ultimate control. Important characteristics consist of:
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC): Automatically modifies the car’s speed to keep a safe distance from the vehicle in front of it.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB): Brakes automatically in the event of an impending collision to help avoid or lessen an accident.
- Lane Keep Assist (LKA): When pulling out of the lane, counter-steer to help retain the car in its lane. unintentionally.
- Semi-Automated Park Assist: Helps drivers park by giving them direction and, in certain situations, controlling the steering autonomously.
Level 2 – Conditional Automation
In certain circumstances, Level 2 ADAS technologies enable more hands-off driving. Drivers need to be alert and prepared to take over. Key characteristics include:
- Highway Driving Assist: Automatically adjusts speed and steering on highways by combining ACC and LKA (Lane Keeping Assist).
- Traffic Jam Assist: Regulates stop-and-go traffic by braking and accelerating in the designated lane automatically.
- Automated Parking Assist: During parking maneuvers, assumes total control over the steering, braking, and acceleration.
Level 3 – Limited Automation
Driver assistance ends with Level 3 and is replaced by limited automation.
In some situations, drivers may activate the system; nevertheless, they must be ready to regain control at any time. Important characteristics consist of:
- Conditional Automated Driving: Manages braking, acceleration, and steering under specific situations, enabling drivers to momentarily take their eyes off the road.
- Highway Pilot: Allows for the use of autonomous vehicles on highways under certain circumstances, relieving drivers of the need to actively operate the vehicle.
Level 4 – High Automation
Level 4 represents high automation, meaning that under certain circumstances, the car can manage every aspect of driving. Unless an unforeseen circumstance arises, drivers are not expected to step in. Important characteristics consist of:
- Autonomous City Driving: Autonomously controls traffic and city streets, avoiding obstructions like pedestrians and crosswalks.
- Valet Parking: Parks the car automatically without the need for driver assistance.
- Personal Mobility Assistant: Transports people autonomously on demand, picking them up and putting them off at predetermined destinations.
Improved Efficiency
AI in the automotive sector can reduce traffic jams and improve fuel economy. The fuel economy of driverless cars could decrease by 10%.
Artificial intelligence systems assess traffic patterns and road conditions to recommend the most efficient driving routes, which lowers fuel use and pollutants.
Additionally, intelligent traffic management systems driven by AI can regulate flow to reduce congestion.
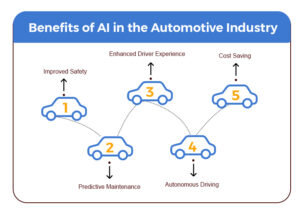
Benefits of AI in the Automotive Industry
The use of AI technology in the automotive sector is expanding as a means of streamlining processes and enhancing overall vehicle performance.
Artificial intelligence has changed how automobiles are designed, made, and operated by utilizing the potential of big data, IoT, AI, and ML in the automotive sector.
The benefits of AI in the automobile sector are tremendous, ranging from driverless vehicles to cutting-edge safety systems.
 Improved Safety
Improved Safety
The increased level of road safety is one of the major benefits of AI for the automotive sector.
Lane departure warning (LDW), autonomous emergency braking (AEB), and adaptive cruise control (ACC) are three very effective security systems.
These three security systems use AI to warn drivers of possible hazards, prompt them to take action, and avert deadly accidents.
Predictive Maintenance
The increased level of road safety is one of the major benefits of AI for the automotive sector.
Lane departure warning (LDW), autonomous emergency braking (AEB), and adaptive cruise control (ACC) are three very effective security systems
These three use AI to warn drivers of possible hazards, prompt them to take action, and avert deadly accidents.
Enhanced Driver Experience
The individualized experiences that passengers and drivers receive via AI-powered entertainment make their trips safer, more intelligent, and more entertaining.
For instance, smart voice assistants in cars may play music, provide directions, control the temperature, and more while also understanding the users’ regional language.
Autonomous Driving
A few years ago, the idea of self-driving cars cruising down the highways seemed science fiction, but now, automated vehicles dominate the market.
With the promise to decrease accidents, increase mobility, and improve traffic flow for physically disabled persons who are unable to drive, this autonomous driving technology has given the industry a new competitive edge.
It has also given drivers a completely new driving experience.
Cost Savings
Costs across all areas of operations, from designing to production, have been dramatically reduced as a result of AI adoption in the automobile sector.
AI may assist in cost reduction in several ways, including by streamlining supply chains, enhancing manufacturing processes, and spotting possible problems in cars.
Overall, the development of AI has significantly aided the expansion of the automotive sector and changed how we interact with and operate our automobiles.
Use Cases of AI in the Automotive Industry
The application of AI in the automobile sector is extensive and varied.
Artificial intelligence is used throughout the life cycle of a car, from design and manufacture to sales and maintenance.
Top automotive firms work hard to incorporate AI into their cars because of this.
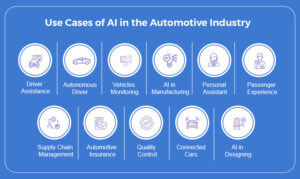
Driver Assistance
- One of the best applications of AI in the automobile sector is driver assistance.
- AI-enabled systems use sensors to help drivers navigate, detect pedestrians, keep an eye on blind spots, and warn them when something is amiss so they may take action to avoid accidents.
Autonomous Vehicles
- In the automotive sector, autonomous vehicles the next-generation cars with self-learning and self-driving capabilities are in fact the ideal use of artificial intelligence.
- With the use of AI technologies like machine learning, deep learning, big data, etc., self-driving cars may operate largely autonomously while still adhering to traffic regulations and safe driving practices.
- While there are still some regulatory challenges in completely visualizing the concept of autonomous vehicles, we are closer to experiencing driverless cars roaming around on the road than one may think.
Driver Monitoring
- AI algorithms keep track of who is driving the car the usual driver or a passenger and when the regular driver is in the driver’s seat, they automatically change the mirrors, the seat, and even the temperature.
- In order to identify tiredness and awaken the driver, AI systems also track the position of the driver’s head and eyes.
AI in Manufacturing
- Manufacturing is a key component of the automotive sector, where even a tiny mistake can have negative effects.
- However, the development of AI technology can greatly advance and streamline the automobile manufacturing process.
- For instance, picking parts off conveyor belts manually is a labor-intensive and inefficient way to finish the car-making process.
- Robots can now independently select parts, reducing the need for human interaction and accelerating the manufacturing process thanks to AI technologies.
- Robots also warn people when a machine unexpectedly fails, avoiding any accidents.
Personal Assistant
- Although automakers frequently prefer to integrate third-party voice assistants like Alexa and Siri, other firms in the market opt to develop their own voice-recognition software.
- Making calls, adjusting the temperature, changing the radio station, playing music, letting the driver know how much gas is left in the tank, and many other tasks are made possible by AI-enabled personal assistance in cars.
- The ability of voice recognition programs to be highly personalized in other words, to remember the user’s preferences and make suggestions based on past behavior is its most significant feature.
Passenger Experience
- Automotive manufacturers work to enhance their vehicles with all viable AI technologies, such as IoT, picture data, NLP, and object identification, taking into account the experience of passengers and safety on the road.
- Additionally, particular commands enable passengers to purchase meals, listen to their preferred music, and engage in other enjoyable activities while on the road.
Supply Chain Management
- AI in the automotive sector is a useful invention for effectively managing its intricate supply chain components.
- Automotive managers face a daunting task in tracking the transit of the components and their arrival at the destination places because a single car has about 30,000 different parts that come from all over the world.
- The process of manufacturing cars is quite difficult due to the complicated nature of importing various vehicle parts. In this case, manufacturers can design a fully automated system to effectively manage the supply chain system, adjusting quantities and routes to the anticipated spikes in demand for parts. This is made possible by integrating AI and ML in the supply chains.
Automotive Insurance
- AI in vehicle insurance has many advantages for both drivers and insurers. In the event of a mistake or tragic accident, AI algorithms speed up the insurance claim process.
- The driver can effortlessly fill out claims and collect incident data thanks to the AI’s object detection, picture dataset, and other features.
- In order to avoid disputes and expedite the claims processing process, AI is used by insurance firms to interpret photos and analyze car damage effectively.
Quality Control
- The primary goal of a car owner is to keep a high customer base by maintaining the quality of their vehicles. However, manual inspection of vehicles may result in a lower rate of defect discovery, a slower rate of problem resolution, and a longer turnaround time.
- In contrast, AI-based data annotation enables manufacturers to find even the smallest problem in the vehicles at an early stage and notify them so they can fix it before it becomes essential. Which car parts require replacement and which require maintenance are made clear to consumers by an AI system.
Connected Cars
- Autonomous driving is now considerably safer and more enjoyable because of the quick expansion of IoT use cases in AI systems that allow infrastructure, smart watches, mobile phones, and vehicles to communicate with one another.
- For example, networked vehicles can talk to one another on the road to keep a safe distance. Additionally, connected vehicles assist traffic controllers in effectively managing traffic flow by giving them a more comprehensive view of the state of the road.
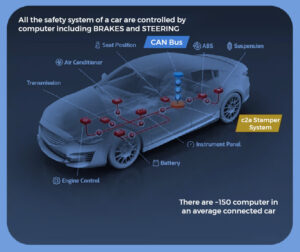
AI in Designing
- Automobile producers must deal with a variety of responsibilities, from sketching out concepts for a car model to designing it in the same way, which can take a lot of time.
- However, with AI in the automotive sector, producers and architects may complete real-time tracking, programmable shading, and other tasks much more quickly to complete the car design process.
- AI reduces the time required for design approval and sanction by enabling a quicker and better design workflow. Additionally, AI picture databases aid manufacturers in producing a variety of designs for improved product concepts and processes for autonomous vehicles.
These are just a few of the many ways artificial intelligence is being used in the automotive sector to redefine the business and potentially change how cars are built, produced, and operated.
Generative AI in the Automotive industry
Roadside assistance and vehicle manuals are being significantly impacted by generative AI in the automotive sector.
Utilizing generative AI in the automobile industry requires a methodical and deliberate strategy in order to fully utilize the technology.
The benefits of generative AI for the automotive sector are listed below.
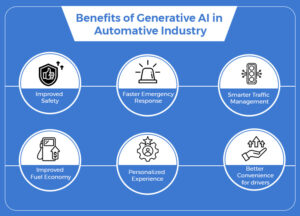
The benefits of applying generative AI in the automotive sector are:
Improved Safety
The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) technology has led to the development of enhanced safety systems that notify drivers of potential hazards, take preventative action, and avert catastrophic collisions, thereby improving road safety for all.
Faster Emergency Response
When an accident occurs, AI can expedite emergency response times by automatically notifying emergency services.
Smarter Traffic Management
By analyzing real-time traffic data, artificial intelligence can suggest other routes for emergency vehicles, avoiding congested areas and cutting down on the amount of time it takes to get to the scene of an accident.
Improved Fuel Economy
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can assist fleet managers in identifying opportunities for increased fuel economy by analyzing fuel consumption data and identifying patterns and trends.
Artificial Intelligence has the potential to offer substantial suggestions for fuel economy and cost reduction by examining features like idle time, vehicle speed, and route efficiency.
Personalized Experience
The driver’s past actions, preferences, and requirements may be used by the AI in-car to give a more customized experience.
The ability to personalize climate settings, audio, navigation, and other features improves and becomes unique to each driver.
Better Convenience for Drivers
By automating navigation, route planning, and even autonomous driving functions, artificial intelligence (AI) can increase driver productivity.
Artificial intelligence-powered GPS and navigation systems can provide drivers with the best possible routes, real-time traffic updates, and adaptive driving aids, freeing up their attention and making driving more convenient and stress-free.
Challenges of AI in the Automotive Industry
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology has advanced significantly in the automotive sector, enhancing user experience, safety, and efficiency.
To properly incorporate and use AI, the automobile industry must overcome several obstacles, including the following:
Data Privacy and Security – Large volumes of data, including information on driver behavior, location, and car diagnostics, are produced by connected automobiles. The security and privacy of this data must be guaranteed, which is a difficult task. Data breaches or unauthorized access can have serious repercussions.
Regulatory Compliance – The integration of AI technologies may necessitate major revisions to satisfy these requirements because the automotive industry is subject to a variety of laws and standards. It can be challenging to navigate these rules as AI capabilities advance.
Safety and Liability – Determining responsibility in the event of accidents or malfunctions becomes more difficult as AI systems take on more crucial responsibilities in automobiles. Setting up precise rules for accountability is crucial.
Ethical Concerns – Choosing between two potentially detrimental outcomes is one of many complicated moral and ethical considerations that AI algorithms in autonomous vehicles must make. It is a huge difficulty to define these ethical standards and make sure the AI operates ethically.
Data Quality and Diversity – For training, AI systems need a variety of high-quality data sources. It can be difficult to ensure that data adequately depicts the different situations that cars may face when driving, such as weather, traffic, and other factors.
Testing and Validation – It’s a difficult challenge to verify the dependability and safety of AI-driven vehicle systems. It is a huge problem to provide rigorous testing methods that imitate real-world scenarios and guarantee that AI systems operate consistently under all circumstances.
Interoperability – Vehicles must communicate with one another and with infrastructure as they grow more autonomous and connected. It is difficult to guarantee that the systems and vehicles from various manufacturers can work together seamlessly.
Cost – It can be costly to develop and integrate AI technologies. Both producers and customers may find it difficult to balance the price of new technologies with their advantages.
Consumer Acceptance – It can be difficult to get people to trust and use autonomous vehicles that are powered by AI, particularly when worries about reliability, safety, and privacy are still present.
Infrastructure Readiness – The ability of infrastructure, such as 5G networks and smart highways, to support connected and autonomous vehicles will also determine how widely AI is adopted in the automotive sector.
Talent Shortage – The number of qualified AI and machine learning experts who can work on automotive AI projects is in short supply. In this industry, talent attraction and retention are essential.
Maintenance and Updates – Ensuring the long-term reliability and security of AI systems in vehicles requires ongoing maintenance and updates. Managing these updates and ensuring they do not disrupt vehicle operations is challenging.
Top 4 Automotive Companies Using AI Solutions

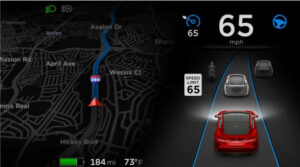
Tesla – Tesla made waves by introducing artificial intelligence to the auto sector. Their vehicles use AI algorithms for decision-making and driving control to operate on advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving capabilities.
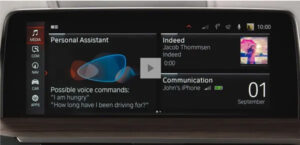
BMW – BMW also incorporates AI into its infotainment, driver assistance, and other car features. The Intelligent Personal Assistant from the top automaker uses natural language processing to provide voice-controlled interaction and individualized experiences.
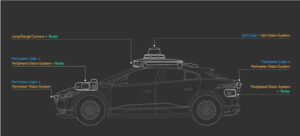
NVIDIA – NVIDIA provides computing platforms and technologies for AI to the automotive industry. The business’s Drive platform gives autonomous vehicles artificial intelligence features like perception, mapping, and route planning.

Waymo – The company Waymo, a division of Alphabet Inc., is regarded as a leader in the field of autonomous driving. A self-driving system that makes use of artificial intelligence for navigation and reaction to the surroundings has been successfully implemented by the corporation.
Future of AI in the Automotive Industry
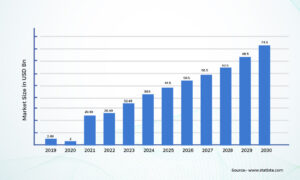
According to Next Move Strategy Consulting, the global automotive intelligence market is projected to grow between 2019 and 2030. While the market was sized at some 2.5 billion U.S. dollars in 2019, it is expected to reach the size of around 74.5 billion U.S. dollars in 2030.
As a whole, the automobile sector is about to undergo a significant upheaval because of advances in artificial intelligence.
The world is being overtaken by AI in the automotive sector, and many automakers have already made great progress in designing and building smart automobiles.
Artificial intelligence is what will enable the automation of the automotive sector in the future.
AI is poised to bring about a huge revolution, transforming the sector and elevating it to new heights.

Conclusion
In conclusion, AI is radically changing the car industry and bringing about safer, smarter, and more environmentally friendly vehicles.
Autonomous driving, predictive maintenance, and sustainable practices are becoming a reality with the integration of AI, ensuring increased safety and effectiveness.
To fully realize the potential of AI in changing the automobile scene into a safer and more sustainable future, privacy, ethics, and regulatory issues must be addressed.



 Improved Safety
Improved Safety






