Image and Video Processing in Defense and Military: In today’s rapidly changing defense and military environment, image and video processing is one of the most critical technologies that allow our forces to think smartly, speedily, and accurately.
Advanced image and video processing technologies allow soldiers and analysts to find objects, track movement, and understand what threats may come from in real time.
Through advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence, these technologies bring a clearer view of what is going on on the ground, which helps respond to events more promptly and effectively.
This capability can make the difference between mission success and failure when difficult and unpredictable environments are involved.
Other than intelligence, they are also paving the way toward breakthroughs in autonomous systems and smarter unmanned vehicles that better equip the fighting force with the tools they need to stay safer and better informed.
As military operations continue to evolve, image and video processing is morphing how we gather, interpret, and act on critical information on the battlefield.
In this blog, we’ll explore the transformative impact of image and video processing in military applications, diving into the latest technologies, real-world examples, and how these advancements are reshaping the future of defense.
Image Processing in Military Applications and Requirements
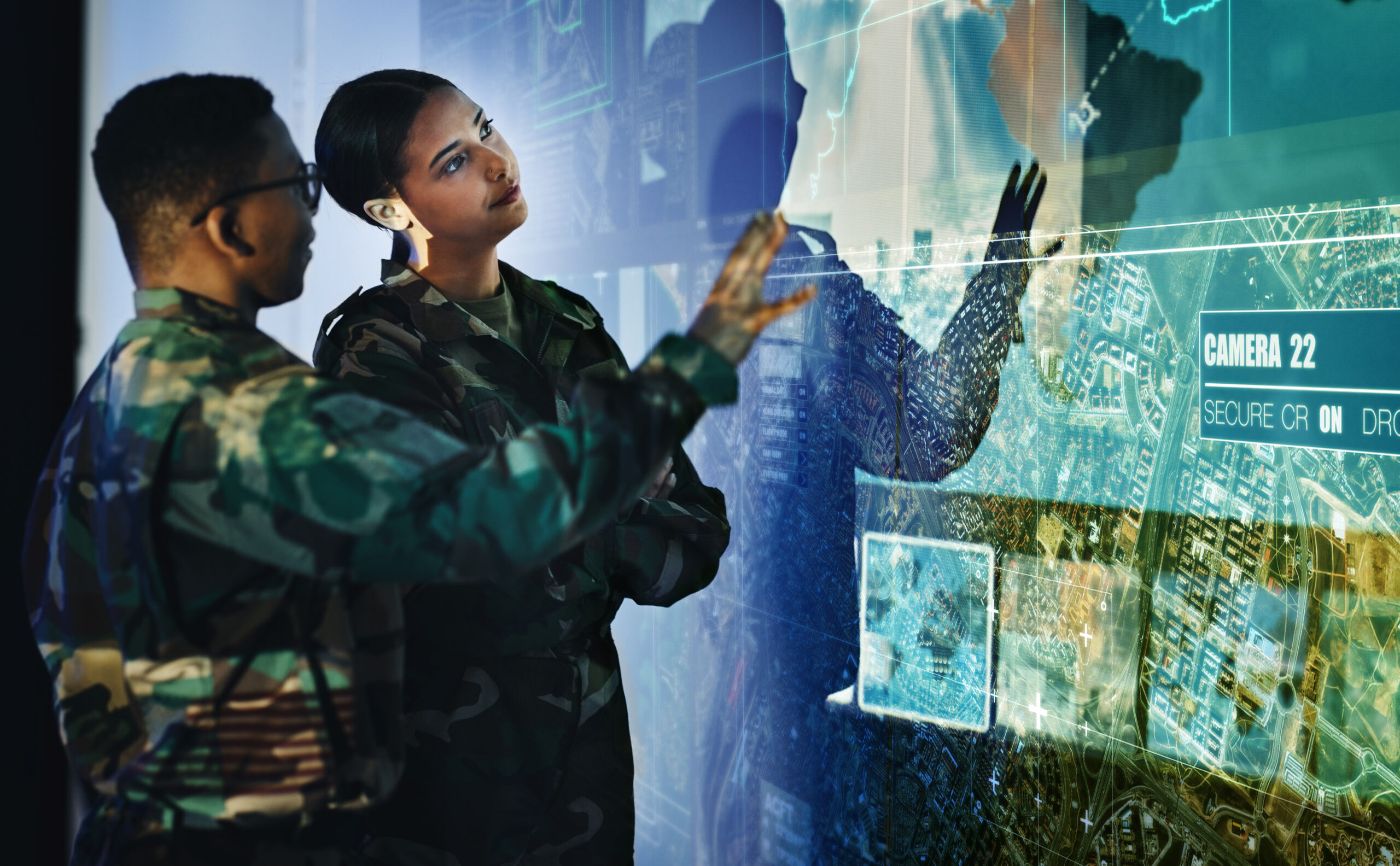

Digital image processing has been extensively used in defense and security applications, including vehicle navigation, missile guidance, automatic/assisted target recognition, small target detection and tracking, and wide-area surveillance.
Reducing the workload of human analysts to handle the constantly growing amount of image data being gathered is one objective of an image processing strategy in defense and security applications.
The development of methods and algorithms that will greatly facilitate the creation of completely autonomous systems that can make decisions and take action based on all sensor inputs is a second, more difficult objective for image processing researchers.
Target tracking by object recognition from a high-definition camera on a surveillance truck is one of the many uses for image processing technology. As varied as the applications that need image processing are the products that offer it.
Remote Sensing
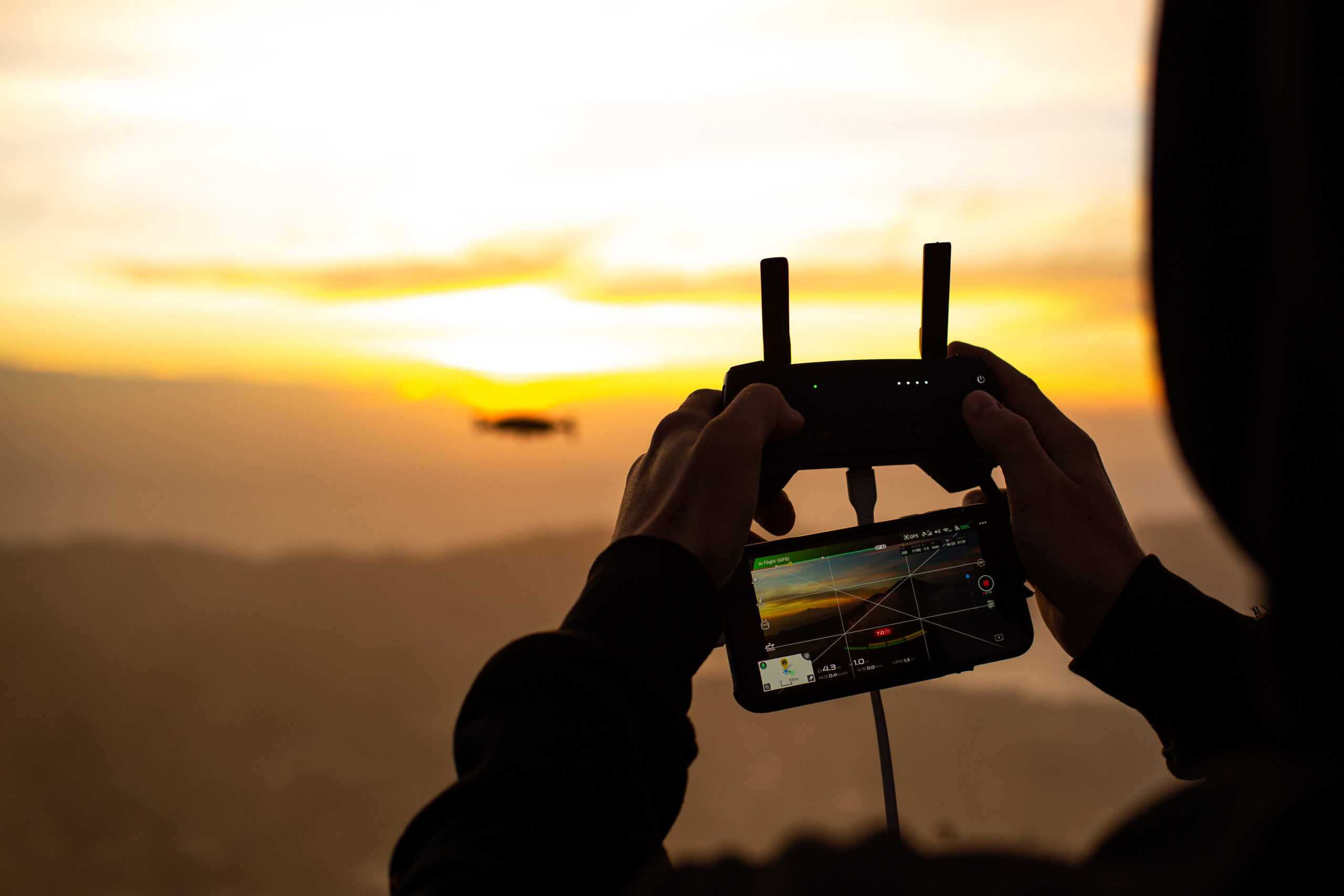

Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and hyperspectral imaging are two examples of remote sensing technologies that use image processing techniques to gather and analyze useful data about the Earth’s surface from a distance.
Terrain mapping, environmental monitoring, and identifying enemy camouflage and concealment tactics are some military uses for remote sensing.
With the use of these skills, military planners can more accurately plan operations and obtain important insights into the operational environment.
For a variety of reasons, including the requirement for autonomous operation and the necessity to leverage the outputs from a wide variety of complex sensors, image processing is becoming more and more significant in defense systems.
The data is becoming a potent instrument for managing and exploiting resources to fulfill global demands. To capitalize on the new kinds of data, new techniques for analysis are being created.
Satellites may even be used to detect hostile minefields at the tactical level. On a strategic level, image processing is crucial for identifying and counting missile silos from reconnaissance photos to verify the arms control agreements.
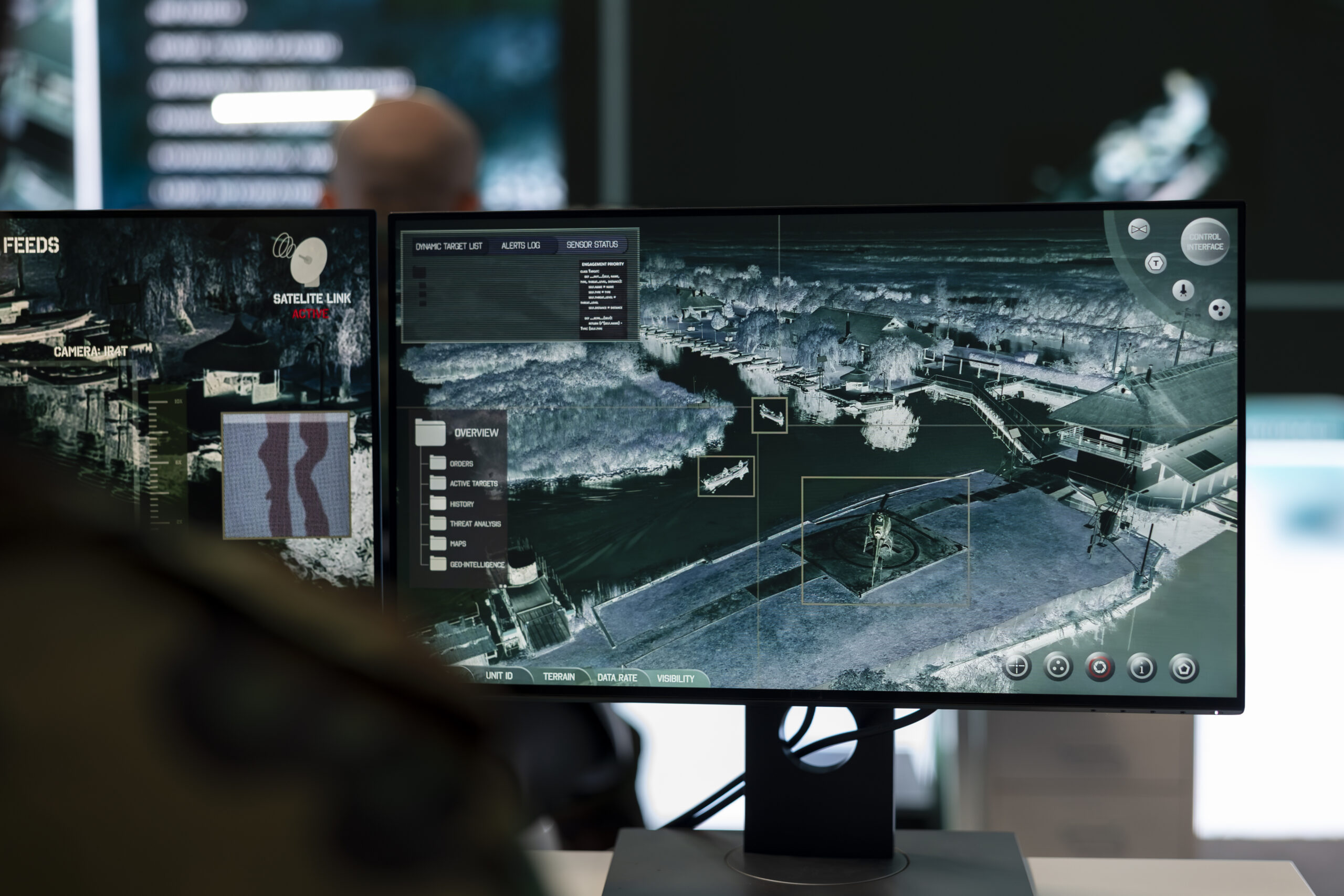
Object Recognition

Object recognition is one of the main uses of image-processing technology in the military.
Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms can recognize and categorize items of interest in real-time by evaluating photos taken by a variety of sensors, including satellites, drones, and security cameras.
This allows military personnel to swiftly evaluate the battlefield environment and spot any threats or targets. It also includes vehicles, soldiers, weaponry, and infrastructure.
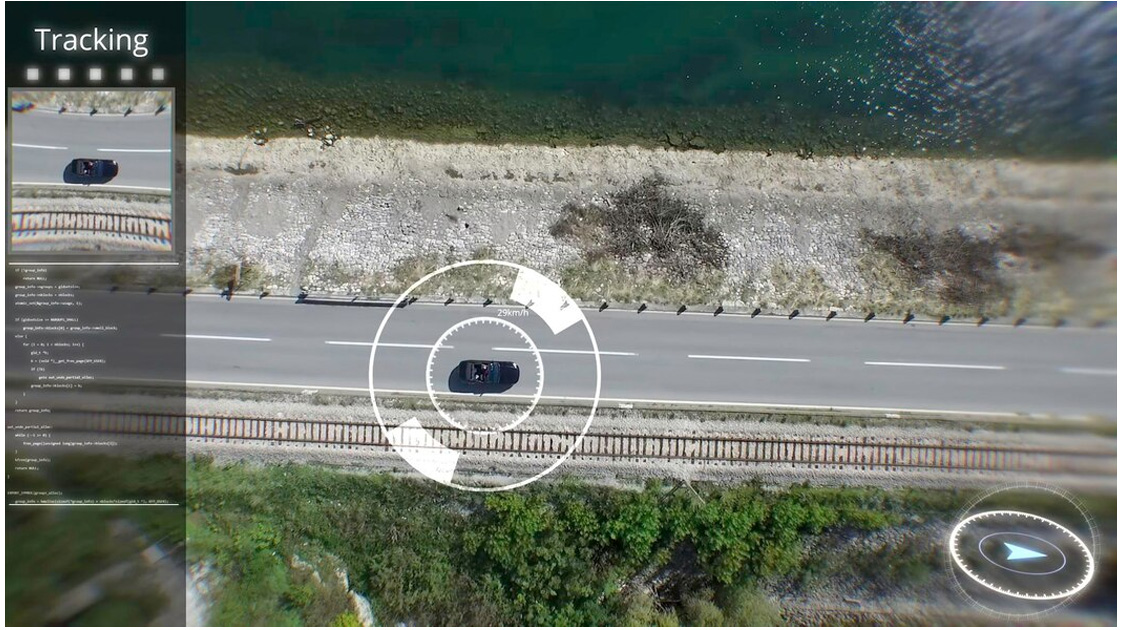
Target Tracking

Target tracking also relies heavily on image processing technology, which enables armed forces to keep an eye on enemy assets’ movements and conduct constant surveillance over valuable targets.
Tracking algorithms can determine the speed and direction of moving objects, anticipate their trajectory, and give commanders and operators real-time updates by evaluating successive photos and extracting important information.
Enhanced Situational Awareness
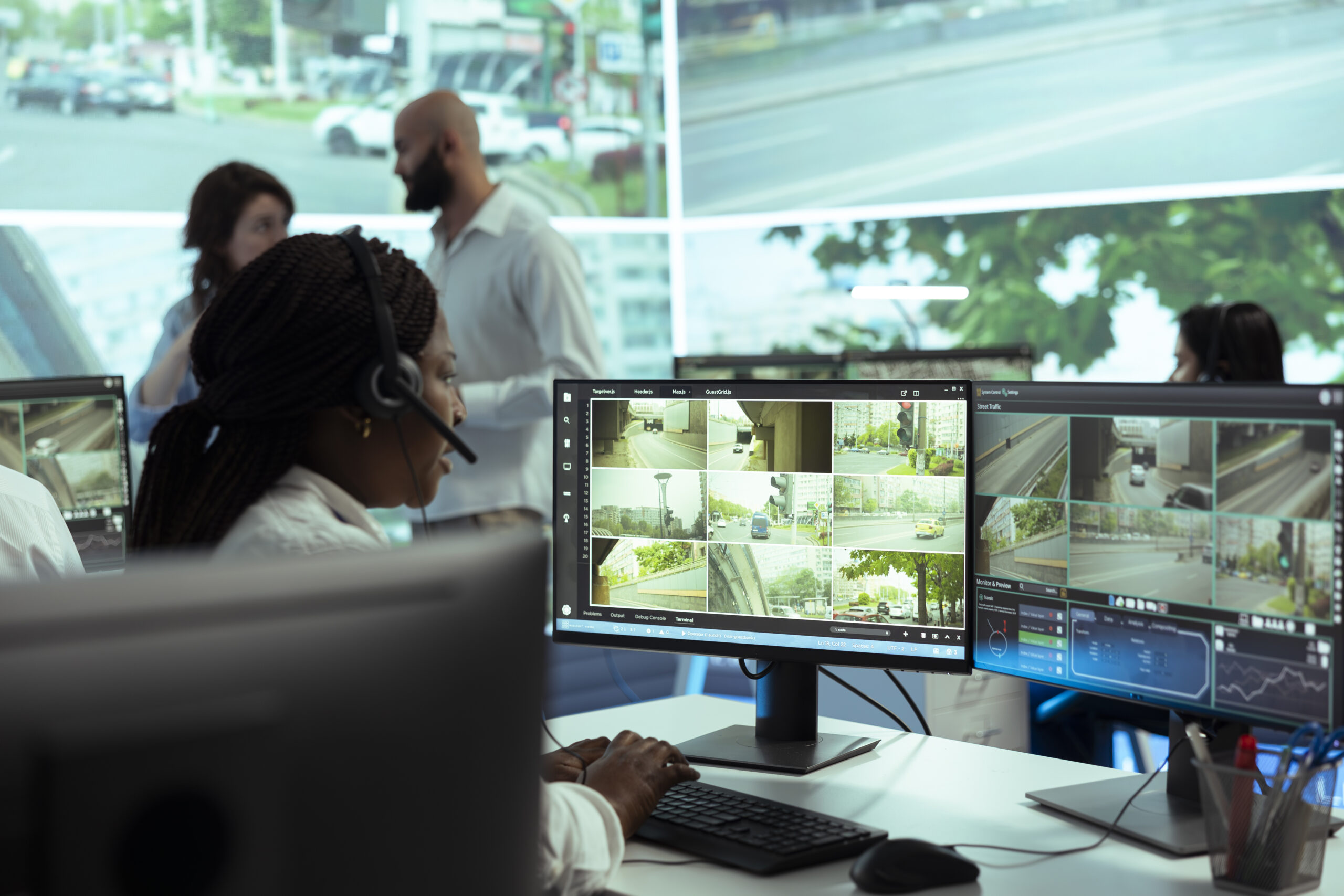

The use of image processing technology to improve battlefield situational awareness is arguably one of its most important advantages for the military.
By giving commanders and soldiers instant access to visual data from many sources, such as satellites, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and ground-based sensors, they may make well-informed judgments and react quickly to opportunities and dangers that change over time.
While image processing technology provides enhanced situational awareness by offering access to a wealth of data from satellites, UAVs, and ground sensors, the growing challenge is presenting this data clearly and quickly.
As military vehicle operators are given more information, the need for high-resolution displays capable of integrating external camera imagery, vehicle systems, and targeting data becomes increasingly vital.
The Rise of AI and Machine Learning
A paradigm change in image processing methods is being sparked by the combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), especially for military applications.
The ability to evaluate enormous datasets, identify complex patterns, and make judgments in real-time with previously unheard-of precision has significantly increased with the introduction of deep learning algorithms.
There are several benefits to this combination of AI and ML in military settings, such as:
Automatic Target Recognition (ATR): AI-powered systems with machine learning algorithms may recognize and categorize targets on their own, relieving human analysts of some of their workload and possibly speeding up reaction times.
ATR systems facilitate more nimble maneuvering of military forces and improve operational efficiency by quickly identifying targets in congested settings.
Improved Situational Awareness: AI and ML technologies enable the real-time analysis of battlefield data, giving commanders a thorough understanding of the scenario.
Commanders can gain vital insights into the operating environment by using these systems, which aggregate and process data from several sources, including drone feeds, satellite imaging, and ground sensor data.
Making better decisions and responding proactively to changing dangers are made possible by this increased knowledge.
Enhanced Threat Detection: Artificial intelligence (AI)-driven image processing systems are excellent at identifying and following possible dangers, including hidden or disguised objects like cars and improvised explosive devices (IEDs).
These systems may search through enormous volumes of visual data for abnormalities suggestive of hostile action by utilizing sophisticated pattern recognition algorithms.
This capacity improves military reconnaissance and surveillance operations’ efficacy and strengthens force protection measures.
Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) Operations
ISR in the Military
ISR assets are widely used by military forces around the world, Many nations utilize ISR capabilities for gathering intelligence, conducting surveillance, and performing reconnaissance missions.
ISR systems come in a variety of sizes, from smartphones to satellites. ISR systems collect and evaluate insights from unstructured data. The rapid flow of information enabled by these insights helps warfighters make better decisions.
To position American and partner forces to outmaneuver, outrun, and engage their opponents, the Department of Defense (DOD) mostly depends on ISR capabilities. Fast data sharing is essential for this to take place.
Connecting ISR sensors from all warfighting domains is how DOD plans to do this. Working closely with commanders and weapon systems in the air, sea, space, and land is part of this.
The Department of Defense has found that an exponential increase in ISR data from multiple sources is essential. Valuable intelligence from multiple data sources supports operations and planning.
The military services that provide this information must take the necessary steps to ensure that commanders, weapons, and weapon systems get it accurately.
To manually handle this data, a large workforce would be needed.
It goes without saying that without the proper analytical systems in place to support the decision-making process, they would find it difficult to complete their tasks faster than the enemy in a competitive or combat situation.
The Department of Defense wants to change from a force that relies heavily on personnel and is best suited for field operations to an automated and artificial intelligence-enabled organization that can defeat peer adversaries in contested scenarios to fulfill the demands of the new global strategic setting.
Each military unit must provide cross-domain sensing and analytic capabilities to obtain an informational edge. The Department of Defense keeps using data from various ISR sources to build the workforce of the future.
Role of Video and Image Processing in ISR
Onboard Processing
For aerial and ground surveillance, counter-drone systems, stabilized gimbal payloads, and other sophisticated camera systems, the low-SWaP tactical video processing hardware is perfect.
Its adaptable configuration enables systems integrators to design customized solutions for exact mission requirements.

Video Processing Software
A robust software package that includes tracking, detection, enhancement, and other features. The hardware and software options are flexible enough to be customized to your system’s specific needs.
The hardware solutions are built on the foundation of our video processing software.
System integrators now have an unparalleled opportunity to tailor processing systems to their unique tactical requirements because of the constantly expanding portfolio of software features.

Scene and Object Tracking Software Functions
For gimbal and pointing control, low-latency video tracking software is perfect. Scene tracking maintains the full scene in the frame, object tracking allows specific objects to be followed independently, and persistent video tracking is possible even via blocked views thanks to powerful image processing and motion estimation. Visual geo-pointing allows you to track a scene or several objects.
![]()
Autonomous Systems and Drones- Use of Visual Data
Autonomous drones are useful in the military for reconnaissance, surveillance, and intelligence collection. These drones can be used in hostile or isolated locations to gather crucial data and keep an eye on activities in real time.
Autonomous military drones provide commanders with invaluable situational awareness through their stealthy design and sophisticated imaging capabilities, which facilitate mission planning, threat assessment, and target identification. They improve operational effectiveness and reduce dangers to military personnel.

Drones and UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles)
Although drone technology is a relatively new area of military technology, military engineers swiftly adopted the use of drones in conjunction with artificial intelligence to produce a product that, in some situations, may function on par with human reconnaissance teams.
AeroVironment and Lockheed Martin are examples of how military defense firms are using drones and modern computer vision and image recognition technology to address military issues without putting human lives in danger. Shield. AI-powered drones are allegedly able to navigate uncharted territory without GPS tracking.
Drones that operate on their own might free up military operators to concentrate on more urgent tasks that require their expertise.
Autonomous drones, for instance, can be deployed to keep an eye on the area a group of soldiers has recently cleared during combat to ensure that enemy reinforcements are not preparing to surprise them.
Autonomous drones may provide numerous advantages on the battlefield, and if properly utilized, these advantages could save the lives of military personnel and operators.
This could be the reason why there are so many real-world applications and businesses with great real-world traction in the drone and AI fields.

Satellite Imaging in Military/Defense

An artificial satellite used for military purposes is called a military satellite. The three most frequent missions are military communications, navigation, and intelligence collection.
Use of Satellite imagery in reconnaissance
An intelligence or reconnaissance satellite, also known as a spy satellite informally, is a communications or Earth observation spacecraft that is used for military or intelligence purposes.
In addition to reconnaissance, military satellites serve several vital purposes, such as research, geodesy, and meteorology. The purpose of military satellites is reconnaissance and monitoring.
They give details about the capability of the adversary forces. Often referred to as “spy satellites,” they are employed for military observation tasks such as tracking adherence to the nuclear test prohibition.
Military satellites are also utilized for data collection, analysis, and remote sensing of the earth’s surface. They are useful for weather and weather condition studies as well as geodesy.
Since 2007, the country’s military surveillance and reconnaissance system, which offers specialized military satellite intelligence services, has been in operation. With ISRO putting more and more satellites into orbit each year, the system has only gotten bigger.
Earth observation satellites for military purposes
Earth observation satellites, also known as Earth remote sensing satellites, are satellites that are used or developed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit.
This includes spy satellites and other similar satellites that are used for non-military purposes including mapping, meteorology, environmental monitoring, and more.
The most popular kind are Earth-imaging satellites, which capture satellite images like aerial photography. Other EO satellites, such as GNSS radio occultation, can do remote sensing without creating images.
Thermal Imaging Technologies
Thermal imaging cameras, sometimes referred to as thermal imagers, are devices that pick up the thermal infrared radiation that things emit.
Even in complete darkness, sight is possible because of the radiated infrared energy, which appears as various hues or shades of gray depending on the temperature of the object.
Beginning as a tool for air navigation in the late 1960s, thermal imaging technology saw military use in the 1970s.
The 1980s saw the release of the first commercial thermal imagers, and by the 1990s, improvements in sensor technology had raised resolution and sensitivity.
These days, the security, engineering, medical, fire and rescue, and law enforcement sectors all make extensive use of thermal imaging cameras.
High-definition thermal cameras and the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) for automated threat identification and analysis are the results of recent developments.
These advancements have broadened the uses of thermal imaging, making it an essential instrument for search and rescue missions, predictive maintenance, and even the use of thermal signatures to detect medical issues.
Night vision systems and their reliance on image processing
By definition, night vision technology makes it possible to see in the dark. Created for military applications, it has given the United States a strategic military edge whose worth is measured in lives.
Today, the technology is often used by federal and state organizations for search and rescue, monitoring, and site security.
With the development of image intensification technologies, night vision equipment has progressed from large optical instruments to lightweight goggles.
Battlefield Awareness and threat detection
Battlefield Intelligence
The ability to extract useful information from vast amounts of visual data is another benefit of image processing technology.
Military analysts can determine possible dangers, evaluate adversary intentions, and unearth secret networks or facilities by looking for patterns, anomalies, and trends in photographs.
This information can help with mission planning, execution, and post-mission analysis, and it can influence decision-making at all command levels.
Targeting, surveillance, and command and control operations must all be completed quickly to make sense of a lot of disparate and potentially untrustworthy data.
Advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques, particularly those related to image understanding, will undoubtedly be needed for this.
Control can then be transferred to an autonomous system, which will try to choose a suitable target from the collection of acquired images and launch a suitable reaction.
AI-driven threat detection Intelligence and response in defense
The term “AI threat intelligence” describes the proactive detection, analysis, and response to cyber threats through the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms.
AI uses sophisticated analytics and pattern recognition to find minor signs of compromise, in contrast to conventional cybersecurity techniques that rely on signature-based detection.
The capacity to identify trends and abnormalities in large datasets is what distinguishes AI-driven threat detection.
Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms can detect possible threats that could elude conventional security measures by examining network traffic logs, security warnings, and threat feeds.
Organizations may better prioritize their AI Defense Mechanism efforts and foresee new threats with the use of predictive analytics.
Facial Recognition and Biometrics in Military
The measuring and statistical analysis of an individual’s physical and behavioral traits is known as biometrics. In military settings, this technology is employed for access control and secure identification.
Nowadays, biometric sensors are an essential part of military base security systems since they offer accurate and trustworthy ways to confirm people’s identities.
Facial Recognition

One of the most used biometric techniques for gaining entry to military installations is facial recognition technology. To confirm a person’s identification, this technology examines their distinct facial traits.
It works especially well in high-security settings where prompt and precise identification verification is crucial.
To guarantee that only authorized individuals can enter restricted areas, facial recognition technology is included in security procedures.
There are many benefits to using facial recognition in military environments. It offers a rapid and non-intrusive way to verify identity, facilitating easy and effective entrance procedures.
Furthermore, a multi-layered security system that is more difficult to get around can be created by combining facial recognition with other biometric techniques.
Fingerprint Scanning

Another popular biometric technology in military installations is fingerprint scanning. For safe identification, this technique entails taking a picture of each person’s distinct fingerprint patterns.
Fingerprint scanning is a dependable approach to access control because it is extremely accurate and challenging to fake. It is frequently used to confirm the identification of contractors and military personnel at entrance points.
The implementation of fingerprint scanning technology guarantees that entry to military bases can only be granted to those who possess authorized fingerprints.
When paired with facial recognition and other biometric technology, this approach works very well, creating a strong and all-encompassing security system.
Voice Recognition
To confirm a person’s identification, voice recognition technology examines their speech patterns.
This technique is especially helpful for controlling access in secure locations where hands-free operation is required, such as communication systems.
To improve a military base’s overall security, voice recognition can be combined with other biometric systems.
Identity verification is made easy and effective by the use of speech recognition in security measures, particularly in situations where prompt decision-making is essential.
Additionally, by adding an extra layer of security, this technology makes it harder for unauthorized people to enter.
Iris Recognition

Iris recognition technology confirms a person’s identity by analyzing distinctive patterns in the colored portion of the eye.
Because of its high accuracy, this technique is frequently used with other biometric technologies to provide safe identification.
In military installations, iris recognition devices are placed in high-security zones to guarantee that only authorized personnel can enter.
Iris recognition is a perfect option for military installation entrance because of its accuracy and dependability.
The complex iris patterns are almost tough to duplicate, guaranteeing that the security mechanism is impervious to possible intrusions.
Biometric Sensors and Intrusion Detection
In military facilities, biometric sensors are essential components of intrusion detection systems. These sensors can identify illegal attempts to enter security perimeters and sound an alarm.
By offering real-time notifications and guaranteeing a prompt reaction to possible attacks, perimeter monitoring with biometric sensors improves physical security.
Any unwanted attempts to enter the military post will be promptly detected and dealt with thanks to the installation of intrusion detection systems that use biometric sensors.
This improves the facility’s overall physical security and increases its resistance to possible intrusions.
Integrated Security Systems
Comprehensive security systems that use a variety of biometric technologies are necessary for military installations.
Multiple layers of protection are ensured by combining voice recognition, fingerprint scanning, iris recognition, and facial recognition.
Because of the strong access control and identity verification features of these integrated systems, it is practically impossible for unauthorized people to enter military installations.
A strong defense against unwanted access is produced when several biometric technologies are combined into one security system.
Military installations can make sure that their security procedures are strict and efficient by employing a variety of secure identification techniques.
Enhancing Physical Security with Biometrics

In military installations, biometrics greatly improve physical security measures. Conventional techniques like passwords and key cards are susceptible to fraud and theft.
However, each person’s biometric traits are distinct and difficult to duplicate. Because of its distinctiveness, biometric sensors are the best option for safe identification and access management in military settings.
Only those with validated biometric information can enter sensitive areas thanks to the use of biometric sensors for physical security. This improves the military base’s general security and lowers the possibility of unwanted access.
Security Protocols and Secure Identification
Ensuring the integrity of biometric systems requires the implementation of strong security protocols.
The optimal operation of security systems and biometric sensors is ensured by routine maintenance and updates.
A safe environment is also enhanced by educating military personnel on the value and application of biometric technologies.
Military installations may guarantee that their biometric sensors and security systems are constantly operating at peak efficiency by implementing and following strict security procedures.
This ongoing attention to detail is essential to preserving the facility’s integrity and security.
Perimeter Monitoring and Access Control

Preventing unwanted access to military installations requires efficient perimeter monitoring. A military base’s perimeter can be monitored and access managed with biometric technologies.
Military locations can improve their overall security posture by combining biometric access control with intrusion detection systems.
Access control and perimeter monitoring work together to guarantee that any attempts to enter the military installation are quickly identified and dealt with.
Because of this all-encompassing security strategy, it is challenging for unauthorized people to obtain access.
Deepfake Detection and Countermeasures
Preventing and/or mitigating breaches connected to deepfakes requires building efficient cybersecurity policies, raising knowledge of deepfake dangers and mitigation techniques among people and organizations at high risk of extortion or coercion, and more.
Additionally, deepfakes can disseminate misinformation about military actions or capabilities, which might lead to war.
Preventing deepfake-related military conflicts requires increasing military and intelligence agencies’ knowledge of the dangers posed by deepfake-related military deception, creating efficient detection and reaction procedures, and encouraging international collaboration.
Applications of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in military
AR in Military / Defence services
The utilization of Augmented Reality (AR) in military and defense has become a game-changing solution for several applications as technology develops.
Australia, which is renowned for its dedication to modernization and innovation in the defense industry, has used augmented reality technology to enhance its capabilities.
AR-Based Training and Simulation:
It has been shown that using augmented reality (AR) in military training and simulation is a very successful way to get soldiers ready for real-world situations.
Troops can participate in interactive, realistic, and immersive training exercises thanks to augmented reality apps.
These augmented reality simulations mimic complex mission contexts, urban warfare, and combat situations. With real-time input, soldiers may practice tactical maneuvers, teamwork, and making decisions under pressure.
AR-based training maximizes skill development and preparedness while reducing the dangers and expenses related to live exercises.
VR in military/defense services
The use of VR technologies in military operations has increased dramatically as they have developed. Effective training is one of the most important applications of virtual reality in the military.
These systems provide a safe and economical means of preparing soldiers for a range of combat situations.
In order to improve tactical decision-making, combat methods, and teamwork, trainees can participate in realistic simulations that mimic actual battlefield settings.
It has been demonstrated that VR training improves learning results, increases information retention, and eliminates the need for costly and risky live-fire tests.
Simulation-enhanced situational awareness is another practical use of virtual reality in the military.
Before entering the actual fighting zone, soldiers can acquaint themselves with the terrain, possible threats, and escape routes by using virtual reality technologies to create realistic virtual representations of operating environments.
Enhancing situational awareness can lower the chance of casualties during missions and greatly improve soldiers’ decision-making skills.
Ethical Considerations and the Future of Military Image Processing
The military’s employment of image-processing technology presents ethical questions notwithstanding its possible advantages.
Concerns including invasions of privacy, improper use of facial recognition, and the possibility of autonomous weaponry systems necessitate thoughtful deliberation and ethical advancement.
Image processing will become more and more important in determining how warfare develops in the future as technology advances.
In order to maximize this technology’s security potential and reduce the possibility of unintentional harm, it is imperative that it be used in an ethical and responsible manner.
In conclusion, image processing technology has become essential to contemporary military operations due to its many uses, which improve situational awareness, intelligence collection, and operational efficacy.
Image processing is set to become more and more important in determining the direction of conflict as developments in AI, ML, and sensor technology spur further progress in this area.
At Logic Fruit Technologies, we empower defense applications with advanced image and video processing solutions.
By combining expertise in computer vision, machine learning, and algorithm design, we deliver high-performance vision systems for mission-critical tasks like surveillance, target detection, and situational awareness.
Our innovative approach ensures accurate, scalable, and efficient solutions that redefine defense capabilities globally.







